A sewerage system is the essential infrastructure for the collection and disposal of wastewater, whether civil, industrial or rainwater. It is a pillar of public health and environmental sustainability. Sewerage networks prevent pathogens from contaminating soil and water, protecting ecosystems and human communities.
There are two main types of sewerage systems: civil systems, used in urban and residential areas, and industrial systems, designed to handle more chemically aggressive wastewater. In both cases, it is increasingly important to move towards innovative, durable and environmentally friendly solutions.
How is a sewerage system made?
A sewerage system consists of a network of underground pipes, either pressurised or unpressurised, fittings, collectors and accessory devices. Its main function is to safely transport wastewater to treatment plants or controlled discharge points. The basic elements of the system include pipes, backflow valves, siphons, inspection chambers and chambers accessible for maintenance and inspection.
Sewerage systems are divided into three main categories. Separate systems have separate pipes for white water (rainwater) and black water (domestic wastewater). Combined systems convey both types of wastewater in the same network. Another fundamental distinction concerns pressurised systems, typical of flat or hilly areas where pumps are used, and gravity (non-pressurised) systems, which are more common in urban contexts.
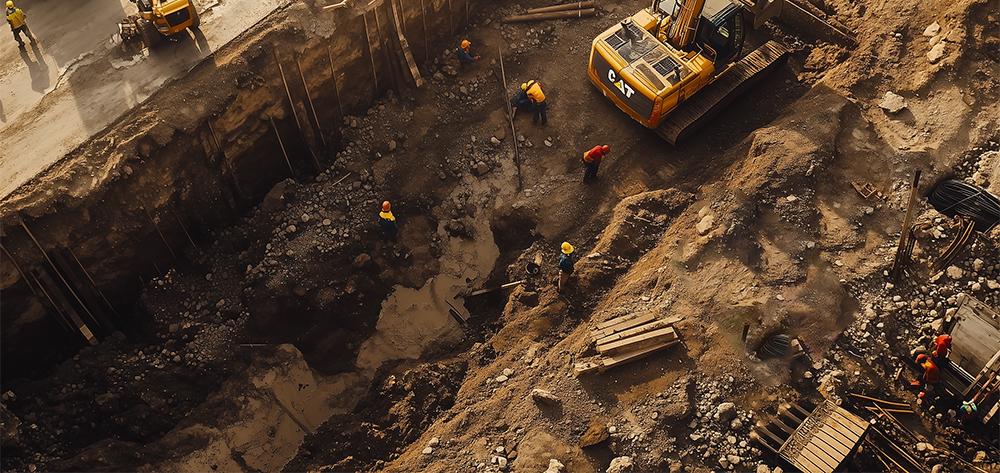

Modern wastewater management faces very specific challenges: increasing urbanisation, the rise in impermeable surfaces and extreme weather events are putting pressure on sewerage networks. In addition, resistance to chemicals and high/low temperatures is essential to ensure durability.
Sewerage systems are essential for public health: they prevent pathogens from contaminating soil and water, protecting ecosystems and communities.
The PPEcoforte system: the ideal sewerage system
PPEcoforte is a high-performance sewerage system designed for non-pressurised underground waste pipes. Composed of triple-layer PP-HM pipes, it guarantees large rigidity (up to SN16), long life and excellent resistance to chemical and mechanical agents. Available in diameters from 110 to 500 mm, it complies with UNI EN 13476 and is suitable for residential, industrial and agricultural applications.
The structure of the PPEcoforte pipe includes an outer UV-resistant layer, a smooth, low-friction inner layer and an elastic load-bearing layer to absorb ground movements. The jointing system uses a two-component locked gasket that prevents slippage and guarantees a perfect hydraulic seal.
The PVC Basicline system: versatility and reliability
PVC Basicline is an equally effective solution made of compact PVC-U. It offers highchemical resistance, a smooth anti-sedimentation internal surface and ease of installation. Suitable for civil and industrial applications, it comes in a similar range of diameters (110–500 mm) and complies with UNI EN 1401.
The PVC Basicline system is also compatible with PPEcoforte. Its fittings are made of PVC with mineral filler for optimum structural and chemical resistance. Joints are available in standard (BL) or with Din-Lock sealed gaskets for larger diameters.
To ensure compliant and durable installation, additional accessories are available: monobloc and telescopic collectors in PE, inspection chambers in HDPE accessible with internal ladder, double-plug siphons and backflow valves to protect against flooding caused by network overload.
Performance and advantages of Valsir drainage systems
The PPEcoforte and PVC Basicline drainage systems offer large performance: resistance to temperatures from -10°C to +95°C, reduced weight for easy handling on site, possibility of complete recycling of materials at the end of their life. These features make the products ideal for modern buildings with a focus on durability and sustainability.
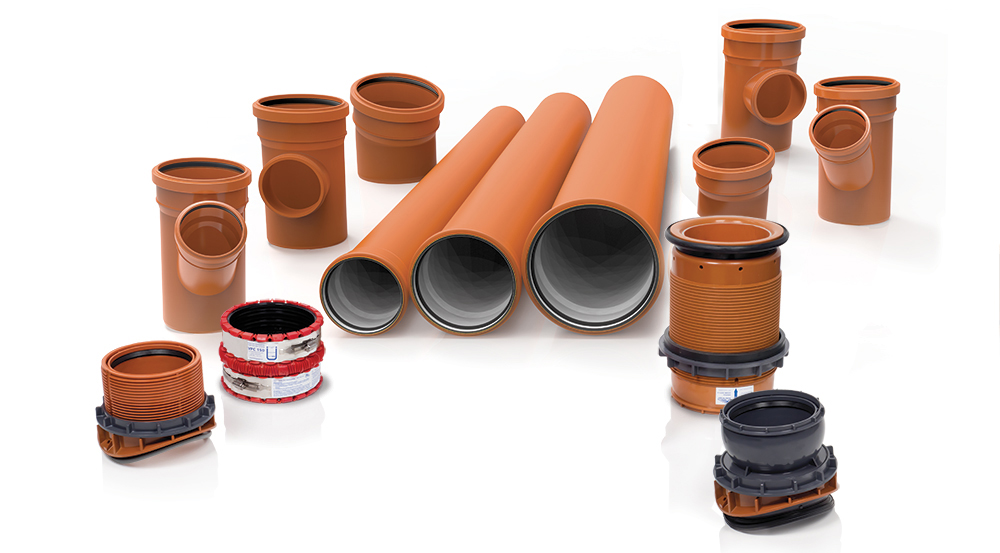

PPEcoforte and PVC Basicline solutions can be used in a wide range of different contexts: residential construction, road infrastructure, industrial and agricultural plants. Their versatility and reliability make them suitable for any plant engineering requirement.
FAQ
What is the difference between pressurised and non-pressurised drainage?
Pressurised drainage uses pumps to transport wastewater, which is ideal in areas without a slope. Non-pressurised drainage uses gravity and is more common in urban areas
What are the main advantages of triple-layer pipes?
They offer high mechanical resistance, excellent hydraulic tightness and long life thanks to the combination of different materials for each layer.
How long does a PPEcoforte or PVC Basicline sewer system last on average?
Over 60 years, thanks to materials that are resistant to chemicals and mechanical stress.
In what contexts is PVC Basicline preferable?
It is ideal for non-pressurised civil and industrial waste, where a lightweight, chemically resistant and easy-to-install system is required.
 Italiano
Italiano
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Français
Français
 Español
Español
 Greek
Greek